- Insomnia and Sleep Disorders
Sleep disturbances can be corrected with targeted brainwave adjustments, helping the body return to natural sleep rhythms. - Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTIntroduction: Understanding Neurotherapy
Neurotherapy is a cutting-edge, non-invasive treatment for a variety of physical and mental health issues that uses brainwave modulation. This type of therapy, sometimes referred to as neurofeedback, trains the brain to self-regulate, providing a customised approach. Neurotherapy, which has its roots in neuroscience and mental health, has emerged as a ray of hope for people who are struggling with chronic pain, stress, anxiety, ADHD, and despair. The significance, advantages, procedure, and typical uses of neurotherapy are all covered in this article to provide you a thorough understanding of this life-changing therapy.
The Science Behind Neurotherapy
At its core, neurotherapy is based on the concept that the brain is capable of neuroplasticity—the ability to change and rewire itself over time. Through sensors placed on the scalp, brainwaves are monitored in real time, identifying patterns that may be contributing to undesirable symptoms such as mood disorders or cognitive difficulties. Once detected, the therapy uses feedback mechanisms to help the brain shift towards more balanced activity patterns. This retraining process not only enhances mental clarity but also promotes physical relaxation and emotional well-being.
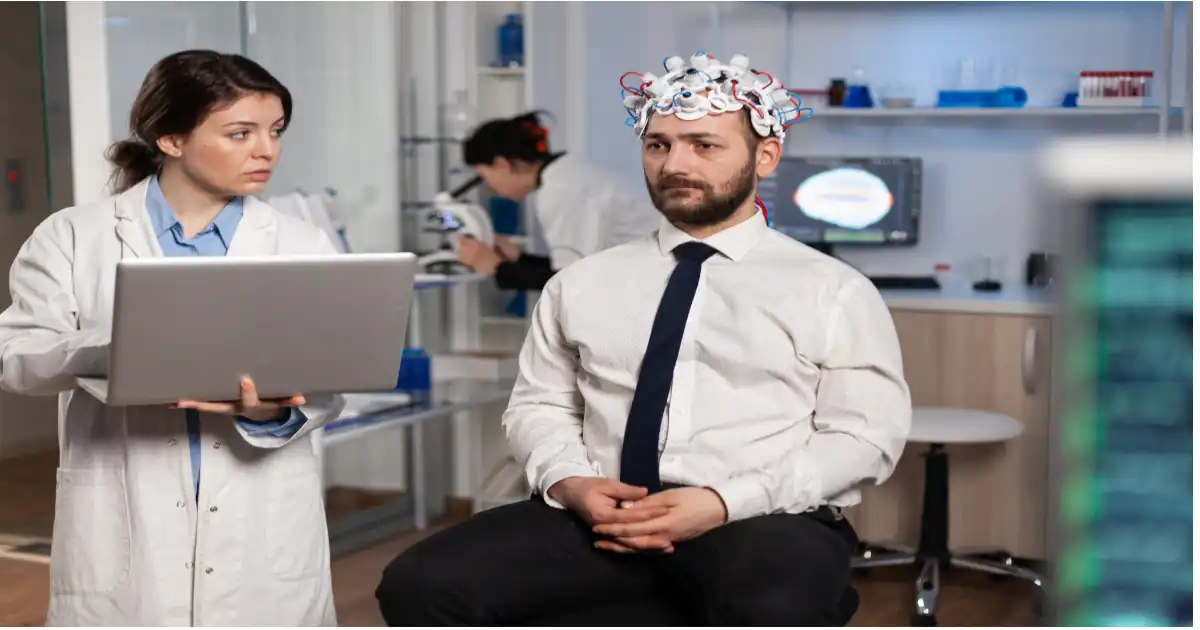
How Neurotherapy Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
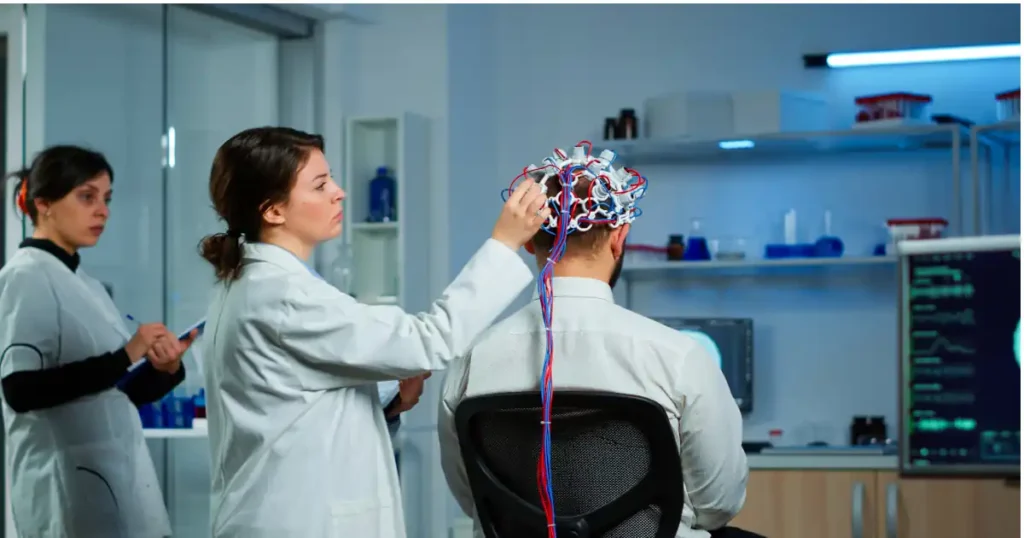
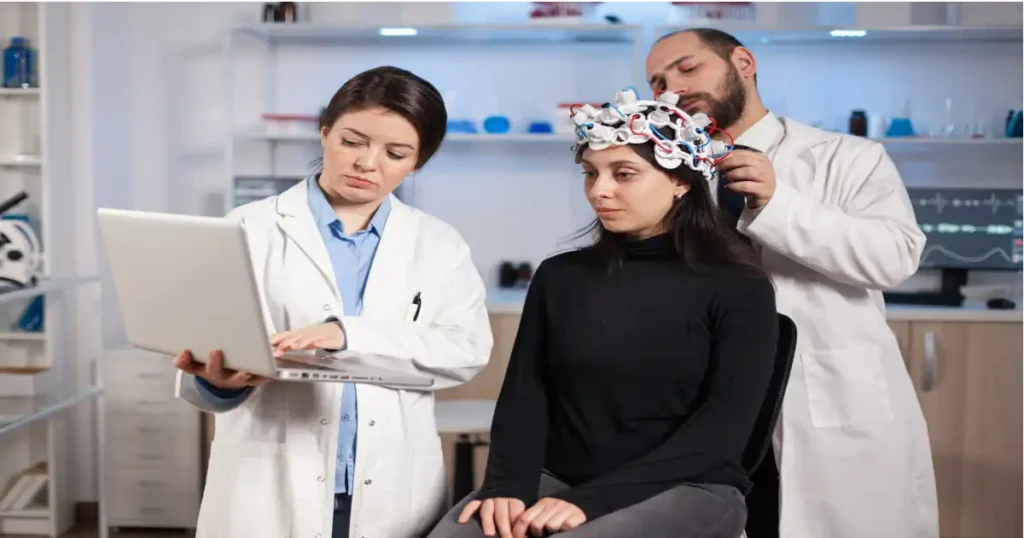
- Initial Brain Mapping
In order to detect any imbalances in brainwaves, electrical activity is monitored in an EEG-based brain map as the initial step in neurotherapy. This map serves as the baseline for designing a custom treatment plan. - Tailored Training Sessions
Based on the brain map, specific frequencies are targeted during training sessions. Using auditory or visual feedback—like sounds or images on a screen—the brain learns to adjust and improve its performance. - Progress Monitoring and Adjustment
Progress is measured over multiple sessions, and the treatment plan is adjusted to meet evolving needs. The brain will progressively learn to sustain good functioning without outside help thanks to this iterative process.
Benefits of Neurotherapy: Unlocking Mental and Physical Potential
Neurotherapy offers a wide array of mental and physical benefits, helping individuals achieve lasting improvements in well-being by balancing brain activity. Its non-invasive, drug-free nature makes it a suitable option for people of all ages. From treating anxiety to enhancing cognitive abilities, neurotherapy has become a transformative solution for various health conditions. Here’s a deep dive into the many ways neurotherapy promotes overall wellness:
1. Reduces Anxiety and Depression Naturally
One of the most significant benefits of neurotherapy is its ability to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression by regulating brainwave activity. Mental health issues often stem from brainwave imbalances, with heightened beta waves associated with stress and reduced alpha waves linked to emotional dysregulation. Training using neurofeedback increases relaxation and mental clarity by assisting the brain in stabilising. Over time, individuals may experience fewer negative thoughts, enhanced mood, and improved resilience to stress.
2. Improves Focus and Reduces Hyperactivity in ADHD
Neurotherapy has shown promising results in individuals with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Through continuous neurofeedback sessions, the brain learns to sustain focus for longer periods and reduce impulsive behavior. Both children and adults with ADHD benefit from the therapy, which trains their brains to manage distractions and hyperactivity effectively. Better academic and professional results are the result of this increase in attention span and cognitive control.
3. Enhances Emotional Regulation and Cognitive Functioning
Emotional instability can lead to outbursts, mood swings, and difficulties in interpersonal relationships. Neurotherapy helps individuals improve their emotional regulation by stabilizing the brain regions responsible for emotional processing. Additionally, cognitive functions such as memory, problem-solving, and decision-making improve as the brain learns to operate more efficiently. Enhanced mental sharpness contributes to better work performance and overall life satisfaction.
4. Promotes Better Sleep Quality
Sleep disorders, such as insomnia, are often caused by irregular brainwave patterns. Neurotherapy targets these irregularities, helping the brain establish a healthier sleep rhythm. Individuals undergoing neurofeedback sessions report falling asleep faster, staying asleep longer, and waking up feeling more refreshed. Better sleep not only improves mood but also strengthens the immune system and supports mental health.
5. Manages Chronic Pain and Migraines
Chronic pain and migraines are complex conditions often influenced by neurological factors. Neurotherapy helps reduce the brain’s sensitivity to pain signals by promoting better regulation of the nervous system. This makes it a viable option for people looking for long-term relief without relying heavily on pain medication. As the brain learns to process pain differently, individuals often experience fewer and less intense pain episodes.
6. Supports Stress Management and Relaxation
In today’s fast-paced world, chronic stress is a common issue. Neurotherapy provides a solution by training the brain to manage stress more effectively. By balancing the nervous system, neurofeedback helps individuals enter a relaxed state more easily. Over time, it enhances the brain’s ability to cope with stressors, reducing symptoms like tension, headaches, and fatigue.
7. Long-Lasting and Cumulative Effects
A significant advantage of neurotherapy is that its benefits are cumulative. With each session, the brain gradually becomes better at maintaining optimal patterns without external intervention. This leads to long-lasting improvements in mental health, cognitive function, and overall well-being. Many individuals continue to experience the positive effects of neurotherapy long after they have completed their treatment program.
Common Conditions Treated with Neurotherapy
- Anxiety and Stress Management
Neurotherapy helps individuals manage stress by regulating brainwaves that are responsible for heightened arousal or fear responses. - ADHD and Learning Disabilities
Research indicates that neurotherapy considerably enhances executive function, memory, and attention in people with learning disabilities and ADHD. - Depression and Mood Disorders
For those experiencing depression, neurofeedback enhances emotional regulation, encouraging the brain to develop healthier patterns.
SD)
Neurotherapy offers a safe space for individuals with PTSD to retrain their minds, reducing the severity of flashbacks and emotional triggers. - Initial Brain Mapping
What to anticipate during sessions of neurotherapy
Depending on the demands of the patient, each neurotherapy session usually lasts 30 to 60 minutes. During the session:
- To track brain activity in real time, sensors are applied to the scalp.
- Auditory or visual cues (like tones or screen animations) provide immediate feedback to the brain.
- Over time, the brain learns to self-correct and sustain desired activity patterns, improving symptoms.
Unlike medication, neurotherapy does not involve invasive procedures or pharmaceutical interventions, making it a safe and holistic approach to healing.
Neurotherapy vs. Traditional Treatments: What Sets It Apart?
- Non-Invasive and Drug-Free: Neurotherapy provides a drug-free alternative for individuals seeking long-term solutions without the side effects of medication.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Every brain map is unique, ensuring that each neurotherapy session addresses specific needs.
- Long-Lasting Results: With consistent training, many individuals experience sustained improvement even after completing the sessions.
- No Age Limit: Neurotherapy can benefit both children and adults, making it a versatile solution for various conditions.
Challenges and Limitations of Neurotherapy
While neurotherapy offers numerous advantages, there are some challenges to consider:
- Requires Commitment: A typical neurotherapy program involves multiple sessions over several weeks or months, requiring time and patience.
- Cost and Availability: Accessible neurotherapy facilities are not available in every area, and some people may find the expense prohibitive.
- Initial Discomfort: Some individuals may experience mild discomfort or fatigue during the early sessions as the brain adjusts to the training.
The Future of Neurotherapy: Innovations and Possibilities
With advancements in technology and growing awareness of mental health, neurotherapy is expected to become more accessible and refined. Research continues to explore new applications, such as using neurofeedback to manage autism spectrum disorders and enhance peak performance in athletes and professionals.
Challenges and Limitations of Neurotherapy
While neurotherapy presents a promising array of benefits for mental and physical health, it is essential to acknowledge the challenges and limitations that may arise during the process. Understanding these obstacles can help potential clients prepare for their journey and set realistic expectations.
1. Requires Commitment and Consistency
Participants in a typical neurotherapy program must be very committed. Most programs involve multiple sessions spread over several weeks or even months, requiring individuals to invest time and energy consistently. This commitment can be challenging for those with busy schedules, family obligations, or work responsibilities. Regular attendance is crucial for the brain to learn and adapt effectively; missing sessions can disrupt progress and lead to slower results. Additionally, clients may need to engage in at-home practices or exercises, further necessitating dedication to the process.
2. Availability and Accessibility
Access to neurotherapy services can vary significantly depending on geographic location. In urban areas, there may be several clinics or practitioners offering neurofeedback therapy; however, in rural or underserved regions, options may be limited. Individuals may have to travel long distances to find a qualified provider, which can be inconvenient and time-consuming. Moreover, even in areas with available services, not all practitioners possess the same level of training or experience, making it essential for clients to research and select reputable providers.
3. Cost Considerations
Another difficulty with neurotherapy may be its cost. Neurotherapy is classified as an alternative treatment and is not covered by many insurance policies. As a result, individuals may face out-of-pocket expenses, which can accumulate over the course of a treatment plan. The cost of each session can vary widely based on the practitioner’s expertise, location, and the specific techniques employed. Even if someone is driven to seek help, the cost of neurotherapy may discourage them from doing so. Therefore, exploring potential financing options or sliding scale fees offered by some clinics may be necessary to make neurotherapy more affordable.
4. Initial Discomfort or Fatigue
As with any therapeutic process, some individuals may experience initial discomfort during the early stages of neurotherapy. This can manifest as mild fatigue, headaches, or temporary emotional fluctuations as the brain adjusts to the new training regimen. While these sensations are usually short-lived and part of the adaptation process, they may discourage some individuals from continuing with the program. It is crucial for practitioners to provide support and reassurance during this period, helping clients understand that such feelings are a normal part of the learning process.
5. Varied Responses to Treatment
Another challenge is the variability in how individuals respond to neurotherapy. While many people experience significant improvements, others may not respond as favorably or may take longer to see benefits. Factors such as the severity of the condition being treated, individual brain chemistry, and commitment to the process can all influence outcomes. This unpredictability can lead to frustration for clients who may have high hopes for their neurotherapy journey.
6. Need for Qualified Practitioners
The success of neurotherapy is highly dependent on the expertise of the practitioner. As neurotherapy continues to grow in popularity, it is essential to ensure that individuals seeking treatment work with qualified and experienced professionals. Unfortunately, the lack of standardized training and certification processes can lead to variations in practitioner qualifications. Clients should research and ask for credentials, reviews, and recommendations before beginning treatment to ensure they receive quality care.
The Future of Neurotherapy: Innovations and Possibilities
As we look to the future, neurotherapy stands at the forefront of mental health treatment, poised for significant advancements and increased accessibility. The convergence of technological innovation and a heightened awareness of mental health issues creates a landscape ripe for new discoveries and applications. Let’s examine the possible advancements and exciting opportunities that the field of neurotherapy may bring.
1. Advancements in Technology
Recent developments in technology have transformed the way brain training is delivered and experienced. For instance, wearable devices that monitor brain activity and provide real-time feedback are becoming more sophisticated and user-friendly. These devices allow users to engage in self-directed feedback training in the comfort of their homes, making brain training more accessible to those who may not have local clinics. As these technologies advance, they might provide more individualised and efficient treatment alternatives that take into account each patient’s unique demands and brain patterns.
2. Enhanced Applications
The future of brain training also promises expanded applications across various domains. Research is actively exploring the potential of feedback techniques to assist in managing a range of conditions, including autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Preliminary studies indicate that feedback can improve attention, reduce anxiety, and enhance social skills in children with ASD. These findings are encouraging and suggest that tailored brain training interventions could play a crucial role in supporting the developmental needs of these individuals.
Moreover, brain training is being examined for its potential to enhance peak performance in athletes and professionals. By optimizing brain function through feedback methods, individuals in high-stakes environments may experience improvements in focus, decision-making, and stress management. Athletes are already beginning to incorporate feedback into their training regimens to gain a competitive edge. As more research validates these applications, the integration of brain training into sports psychology and performance training is likely to increase.
3. Integration with Other Therapeutic Approaches
It’s possible that brain training will become more integrated with other therapeutic methods in the future. Combining brain training with traditional talk therapy or cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) could create a more holistic approach to mental health treatment. This integrative model could enhance the efficacy of both therapies, offering patients a comprehensive toolkit for managing their mental health challenges. Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaboration among psychologists, neurologists, and therapists could lead to innovative treatment plans that cater to the diverse needs of patients.
4. Increased Awareness and Acceptance
As society becomes more aware of the importance of mental health, the stigma surrounding mental health disorders continues to diminish. This cultural shift fosters greater acceptance of alternative and complementary therapies, including brain training. Campaigns for public education and advocacy will be essential in educating people about the advantages and possibilities of brain training. As more people recognize the value of brain training techniques, demand for these services is likely to rise, encouraging more practitioners to enter the field.
5. Research and Clinical Trials
Continued research will be crucial in shaping the future of brain training. Ongoing clinical trials aimed at exploring the efficacy of various feedback protocols for different conditions will provide valuable insights into best practices and treatment outcomes. Additionally, studies focusing on the long-term effects of brain training will help establish its role as a standard treatment option within the mental health landscape. As more evidence accumulates, brain training will gain credibility as a scientifically backed approach to mental health.
6. Global Expansion
Finally, the future of brain training is not limited to one geographical location. With increased globalization and advancements in communication technology, the principles of brain training can be disseminated across borders. This globalization of knowledge will facilitate the establishment of brain training centers in underserved regions, providing access to essential mental health resources for individuals who may otherwise go without. The development of online training programs for practitioners can also contribute to the expansion of brain training services worldwide.
FAQs
How does brain training operate and what is it?
The term “brain training” describes a collection of methods intended to enhance emotional stability and cognitive abilities. Feedback techniques are frequently used to assist people in tracking their brain activity and making real-time modifications. Users can learn to improve emotional regulation, decrease anxiety, and increase focus by participating in particular activities. The goal of these techniques is to support improved mental health and brain function.
What are the benefits of brain training?
The benefits of brain training are varied and include increased cognitive flexibility, better stress management, better emotional regulation, and longer attention spans. After taking part in training sessions, many people say they feel less nervous and more focused. Furthermore, brain training can assist with certain problems like anxiety disorders and ADHD by giving them useful coping skills.
What is the average duration of a brain training program?
Answer: Depending on the individual’s objectives and the particular methods employed, a typical brain training program may span anywhere from a few weeks to several months. The majority of programs consist of several sessions, each of which focusses on a distinct facet of emotional and cognitive development. Achieving the intended outcomes requires dedication and consistency. Within a few sessions, people may begin to see benefits, but longer programs typically result in more noticeable changes.
FAQ 4: Are there any side effects associated with brain training?
Answer: Although brain training is generally regarded as safe, some people may feel a little tired or uncomfortable during the first few sessions as their brains get used to the exercise. It’s critical that participants talk to their practitioners about any issues that come up. As they continue the exercise, most people discover that these early feelings gradually go away and become more comfortable.
Can certain mental health disorders be helped by brain training?
Answer: Yes, brain training has been demonstrated to be successful in treating a number of mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, and ADHD. Feedback techniques have been shown to help people focus better, control their emotions, and create coping mechanisms. To find out if brain training is a suitable supplemental strategy for a given disease, it is crucial to speak with a mental health specialist.
How can I locate a certified brain-training professional?
Answer: Look into nearby clinics, mental health specialists, and online training platforms to locate a certified brain training practitioner. Seek out professionals who possess the necessary qualifications, such as certifications in brain training methods or associated disciplines. Reading client endorsements and reviews can also give you important information about a practitioner’s efficacy and methodology. To discuss your objectives and make sure you’re a good fit, it’s best to set up a consultation.
Read Also: Natural Black Hair Dye: 7 Powerful Secrets to Avoid Common Mistakes!